The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) said its research team has developed an AI-based technology to analyze precisely immunological cell movements in three-dimensions.
The team, led by Professor Park Yong-keun of the Department of Physics and Professor Kim Chan-hyuk of the Department of Biological Sciences at the national university, developed the tech to study the immunological synapse (IS) of CAR-T cells, which are used in cancer-fighting therapies, accurately and systematically.

CAR-T cells are created by transforming T cells extracted from patients using the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). Immunological synapses (IS) are made from injecting CAR-T cells into the body and combining them with target cancer cells, which kill cancer cells.
According to the institute, while CAR-T cells are being recognized as an effective therapy, the molecular biological mechanisms are yet unknown.
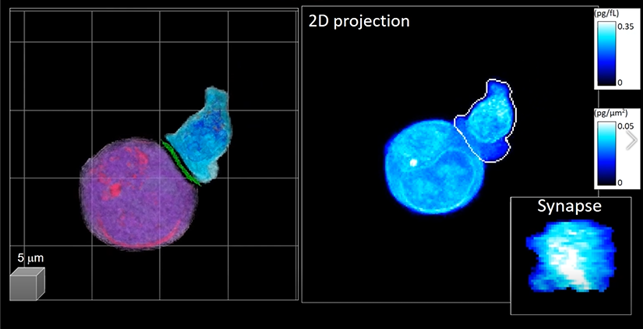
Using 3D holography microscopy technology, the team could quickly measure the interaction between living CAR-T cells and target cancer cells difficult to observe. Although IS-formatted information is deeply related to inducing T-cell vitalization, it is difficult to track with the existing technology, they said.
Researchers also used the technology to track the CAR-T immune gate formation mechanism and confirm the morphological properties of IS related to CAR-T's anticancer effects.
The team expects that the 3D IS data will provide many indicators necessary for the early studies regarding anticancer therapy.
The study results were published in the journal eLife, in December.

