A brief overview of how to obtain a medical license in Korea as a foreigner.
Foreign doctors can treat patients in Korea if they have a Korean medical license. First, they must have a doctor's license from their own country, and then graduate from a medical college approved by the Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. This qualifies them to take the Korea Medical Licensing Examination (KMLE) in Korea.
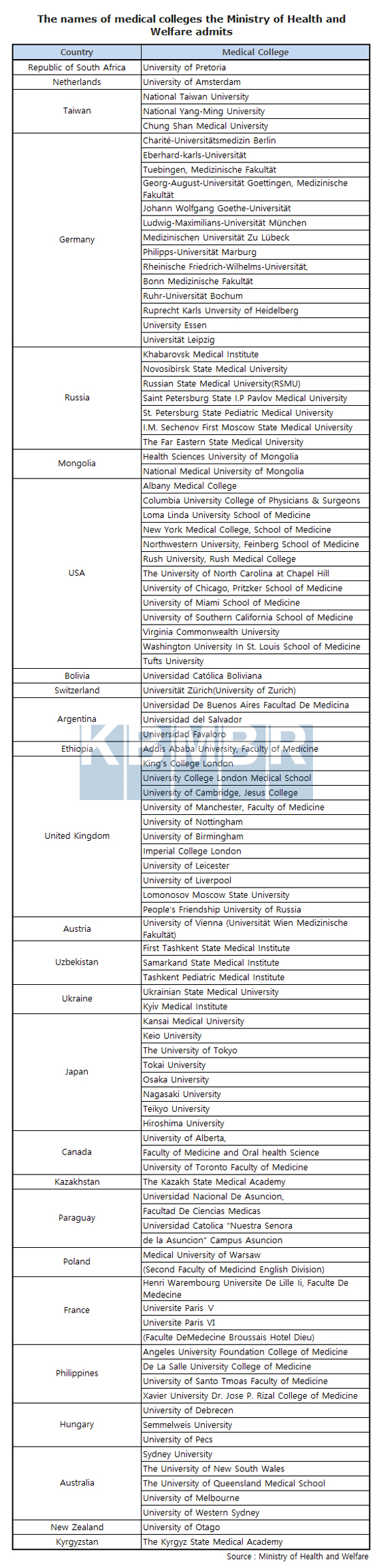
The Ministry of Health and Welfare selects medical colleges by evaluating school systems, curriculums, and academic affairs etc. Currently, it approves 96 foreign medical colleges from 26 countries (chart below).
The U.S.A. has the largest number of medical colleges approved by the ministry (13), followed by Germany(12), England(11), Japan(8), Russia(7), Australia(5), Philippine(3), Chinese Taipei(3), Hungary(3), the Argentine Republic(3), Uzbekistan(3), Canada(2), Ukraine(2), Mongolia(2), Paraguay(2), the Republic of South Africa(1), Netherlands(1), the Republic of Bolivia(1), Swiss(1), Ethiopia(1), Austria(1), Kazakhstan(1), Poland(1), New Zealand(1), and Kyrgyzstan(1).
Upon satisfying the above-mentioned requirements, one must take two tests: the Preliminary Examination and the Korean Medical Licensing Examination (KMLE).
The preliminary examination is required to take the KMLE. The preliminary exam is composed of a written test and a clinical skills test. The test is held every July and August. Applicants must also submit a certificate of TOPIK (Test of Proficiency in Korean) with a level 5 or higher.
Next, the applicant must take the KMLE in the Korean language. The clinical skills test is administrated from September to November. The written test is held in January.
Statistics show that a total of 12 foreigners obtained a Korean doctor's license in the years of 2014 and 2015 (6 in 2014 and 6 in 2015).
For more information, please visit the web site