Kills cancer cells by ‘breaking their means of livelihood’
A Korean research team has developed a new anticancer treatment, which kills cancer cells by destroying mitochondria that supply energy to the cancer cells.
The current cancer treatments remove cancer tissue through surgery and administer chemotherapy drugs. However, continued administration of a chemical can lead to resistance, and when cancer cells become resistant, it is no longer possible to inhibit cancer with synthetic drugs.
To overcome these shortcomings, Professor Ryu Ja-hyoung류자형 and Kwak Sang-kyu곽성규 from Ulsan Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) collaborated with Professor Lee Eun-ji이은지 from Chungnam National University충남대 to develop a new treatment method that removes cancer cells by using the “self-assembly” of molecules. It is a way to cause cancer cells to collapse themselves.
The team specifically targeted mitochondria in cell organelles and synthesized self-assembling materials that would destroy them. When the mitochondria, known as intracellular energy factories, are destroyed, the cancer cells die. The synthesized material is a peptide that links to triphenylphosphonium.
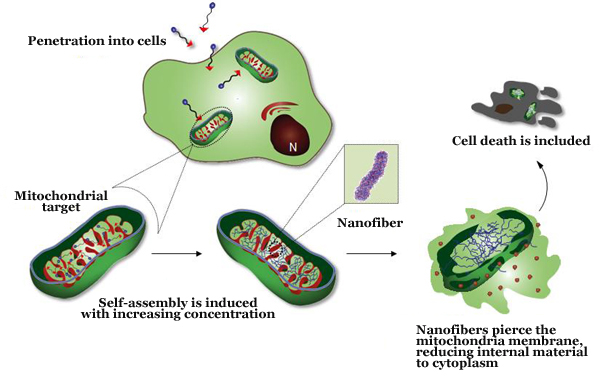
The triphenylphosphonium peptide does not self-assemble outside the cell but exists as a molecule. However, when the particle enters the mitochondria, its concentration increases thousands of times. At this time, the molecules are attracted to each other and assemble themselves to form a nanofiber structure.
The effect of one molecule on the mitochondria of cancer cells is small. However, the influence of the nanofiber structure made up of hundreds or thousands of molecules is so large that it punctures the mitochondrial membrane. This causes the proteins in the mitochondria to come out into the cytoplasm, killing the cancer cells.
"This method can overcome drug resistance by eliminating cancer cells with a unique mechanism than chemotherapy,” Professor Ryu said. "We expect it will lead to the development of therapy for intractable cancer."
The result of their study, titled “Mitochondria localization induced self-assembly of peptide amphiphiles for cellular dysfunction,” was announced on the online edition of Nature Communications on Wednesday.

