Machine learning algorithms that can predict the treatment response of the immunotherapy based on the cancer patient’s clinical information have been developed.
Theragenbio said Friday that it has developed an algorithm that can predict non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patient’s immunotherapy response rate using artificial intelligence (AI). Professors Kim Hye-ryun, Hong Min-hee, Ahn Byung-chul of Yonsei Cancer Hospital’s Oncology Department and Pyo Kyoung-ho at Yonsei University College of Medicine conducted the study.
Due to a combination of various clinical properties in action, it had been difficult to predict the response rate of immunotherapy. However, with the development, it became possible to provide each patient with a more appropriate way of treatment, the company said.
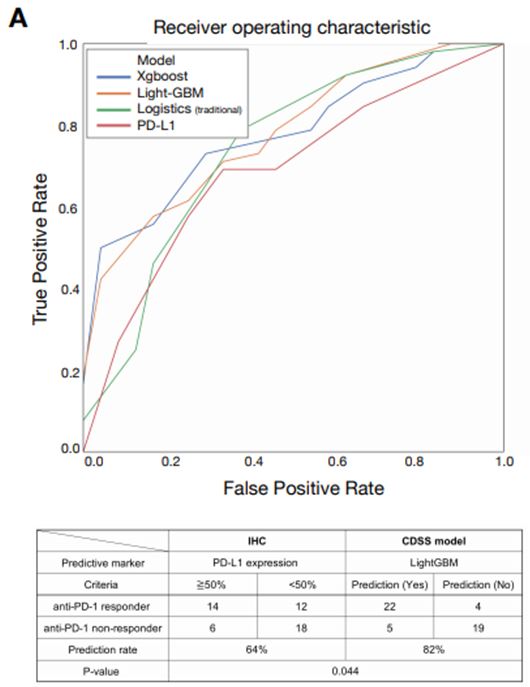
The predictability of companion diagnostic (CDx) response determined by protein expression of programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1), a typical target of lung cancer patients’ drugs, remains at 64 percent.
The research team created algorithms by adopting various machine learning techniques, such as XG Boost and Light GBM, on the data of 142 NSCLC patients going through anti-PD-L1 treatment at the Severance Hospital. This model was than compared with the current one. As a result, the predictability of 82 percent was recorded, 18 percent higher than the current rate.
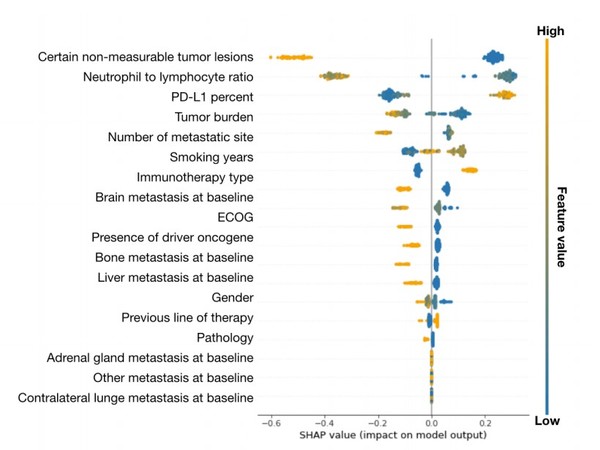
The research used 19 categories of noninvasive clinical data like PD-L1 protein expression, age, gender, the size of the tumor, the location of metastasis, and complete blood count (CBC).
The level of contribution of each agent on the result was found using ‘ensemble analysis’ that associates and makes simultaneous use of diverse machine learning techniques. This would be reflected in additional advancement tasks of the algorithm in the future.
“It is expected that prediction of NSCLC patients’ immunotherapy response would reach high accuracy that would lead to providing best-suited treatment for each individual,” Professor Kim Hye-ryun of Yonsei Cancer Hospital said, “We are planning on conducting a consequent study that could be applied on actual immunotherapy and co-administered trials.”
Theragenbio and the office of research affairs UIF Yonsei University have co-applied for patent rights of the algorithm developed. Consequent studies for clinical trials and commercialization is to follow.
This research has been published in the latest edition of the European Journal of Cancer.