The global contract research organization (CRO) services market is undergoing rapid changes with a surge in clinical trials to develop Covid-19 vaccines and treatments.
Major CROs are clinching merge and acquisition (M&As) deals, and remote clinical trials are expanding.
Following the global trend, the local demand for remote trials is also rising.
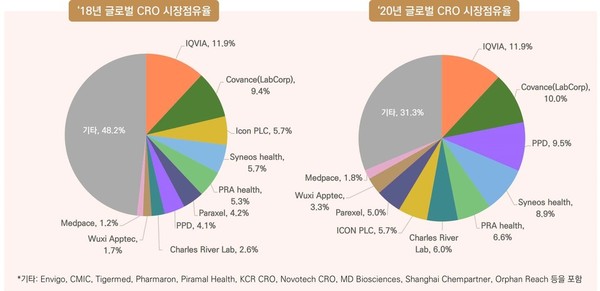
According to the Korea Biotechnology Industry Organization (KoreaBIO) on Wednesday, the global CRO market grew 11.2 percent in 2020 from the previous year thanks to the aggressive development of Covid-19 vaccines and treatments. In the enlarged CRO market, the combined market shares of the top 10 leading CROs have exceeded 50 percent, and their shares are continuing to increase.
M&As among CROs have stalled for several years, but the pandemic accelerated M&A activity among major CROs this year.
Icon, which ranked seventh in the global CRO market in February, acquired the No. 5 player PRA Health Sciences for $12 billion and became the third-largest CRO in the world. The two companies recorded $2.79 billion and $3.18 billion annual sales in 2020, respectively.
In April, Thermo Fisher Scientific, a global reagent and equipment maker in the biotech sector, bought Pharmaceutical Product Development (PPD) for $17.4 billion. Thermo Fisher and PPD posted $32.2 billion and 4.66 billion in sales last year, respectively.
This month, Goldman Sachs said it would take over Parexel, a global CRO, for $8.5 billion. Goldman Sachs and EQT Private Equity, which acquired Parexel, said they decided to invest in the company’s potential in growth in clinical research and innovation.
Remote clinical trials are another change occurring in the global CRO industry. Before Covid-19, patients and researchers used to visit the medical institution for clinical tests. After the pandemic, however, the need for contactless trials has increased because patient enrollment and a visit to medical institutions have become challenging.
Regulatory agencies worldwide have issued emergency guidelines for conducting trials during Covid-19, allowing researchers to use remote monitoring systems to proceed with studies.
Last year, Moderna reportedly minimized study participants’ hospital visits in the clinical trial of its Covid-19 mRNA vaccine by collecting clinical data from participants’ smartphones.
In the future, the demand for virtual clinical trial platforms, eRecruitment (online patient enrollment), and remote monitoring solutions are expected to grow, observers said.
In Korea, however, the regulator has yet to provide an institutional environment for remote clinical trials.
“Remote trial is a global trend. In Korea, it is possible to get electronic patient consent. Still, the cooperation between hospitals and pharmaceutical companies for online trials is insufficient,” KoreaBIO quoted an executive of a local company as saying. “Regulations on protecting personal information are still strict. So, remote trials are not actively carried out.”
Another company official said the government should stop designating clinical trial institutions. Then, various hospitals instead of a few university hospitals will speed up clinical studies, he said.
The country manager of an international CRO at the Korean branch said it was time for Korea to introduce remote clinical trials quickly to perform tests safely and efficiently even in a pandemic situation.

