Amid a global decline in the bioindustry over the past two years, Korea ranked third in Asia in Cytiva’s pharmaceutical and biotech recovery index, the globa life sciences company said.
Korea’s resilience in bio resulted from strong government policies and regulations but the nation lacked investment in human resource and R&D ecosystems, it said.
On this note, Cytiva Korea CEO Choi Jun-ho unravelled the pharmaceutical and biotech recovery index together with industry Insights from its recent 2023 Global Biopharma Resilience Index report at a press conference held on Thursday at Coex, Seoul, on the sidelines of Bioplus-Interphex 2023.
“In the fast-growing Korean pharma and biotech market, fostering talent and improving the R&D ecosystem environment are the most urgent challenges that the government, industry, and academia must address together,” Choi said. “We are committed to fostering domestic bio talent and strengthening R&D through our APAC Fast Track Center in Songdo, Incheon, and various other industry-academia collaboration programs.”
Cytiva’s education center, launched in 2016, provides specialist knowledge in bioprocessing. Choi also noted other human resource training programs with the Korea National Institute of Bioprocessing Research and Training (K-NIBRT) which is expected to launch next year.
Cytiva's resilience index is based on a survey of 1,250 pharma and biotech executives and healthcare policymakers from 22 countries, including South Korea, as well as in-depth interviews with industry experts. Survey participants rated their country's status based on on a scale of 1 to 10 based on five pillars of resilience in supply chain, human resources, R&D ecosystem, manufacturing agility, and government policies and regulations.
This year, the global recovery index was 6.08 out of 10, an overall decline from 2021 (6.6). Supply chain resilience and manufacturing agility, which have seen significant investment during the pandemic, rose slightly, but human resources, R&D ecosystems, and government policies and regulations fell, indicating that they remain a challenge.
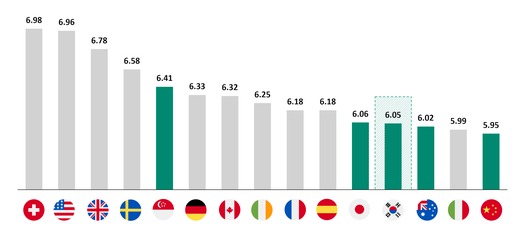
By country, Switzerland (6.98), the United States (6.96), and the United Kingdom (6.78) showed the most promise for the pharma and biotech industry but Thailand (5.36), Saudi Arabia (5.20), and the United Arab Emirates (5.17), which rely heavily on imports, ranked lower.
In Asia, Singapore (6.41) ranked highest, followed by Japan (6.06) and South Korea (6.05).
Specifically, South Korea, which ranked seventh in the world and first in Asia in 2021, dropped to 12th in the world and third in Asia this year.
The rankings reflected Korea’s strong government support and regulatory reform, maintaining its top spot at number four but the other factors such as human resources dropped to 16th and R&D ecosystems dropped to 12th, seeing relatively large declines from two years ago.
The decline in ranking suggests the need to attract talent, create public and private education infrastructure, find R&D partners, and make open innovation a reality reasoned Cytiva’s CEO. Additionally, supply chain resilience and manufacturing agility also received low scores, ranking at 14 and 15 respectively.
The report further noted that there were also positive trends around mid-ranking countries in the index, in particular South Korea, where the government has promised an annual investment of $303 million to nurture the national biotech industry. This investment is accompanied by several regulatory reforms intended to streamline innovation, decentralize clinical trials, and de-risk investment in new therapies, it went on to state.

