The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) said Tuesday that the infectious disease classification of mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, will be downgraded from Class 2 to Class 3 in the four-tier level system starting in 2024.
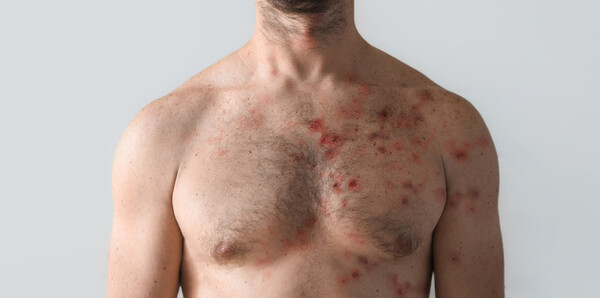
Mpox is an acute, febrile, rash disease caused by infection with the monkeypox virus, a zoonotic infectious disease first discovered in captive monkeys by the Statens Serum Institut in Copenhagen in 1958. Symptoms are similar to those of smallpox, a Class 1 highly infectious disease, but are reportedly milder.
According to the KDCA, mpox causes a variety of symptoms, including fever, chills, swollen lymph nodes, muscle aches, headaches, and respiratory symptoms, and a rash usually appears on the face or mouth one to four days after infection.
Most cases are reported to resolve within two to four weeks of infection. In most cases, symptomatic treatment is sufficient, except in high-risk groups such as immunocompromised patients.
With the revision, the infectious disease classification of mpox will be lowered by one level from Class 2, such as tuberculosis and chickenpox, to Class 3, which is equivalent to tetanus and hepatitis B.
KDCA said that the decision to downgrade mpox's classification was based on expert judgment that infections are sporadic and do not pose immediate danger, aligning it with other Class 3 diseases for efficient management.
Since May 2022, mpox has been spreading in Europe and North America, and the first confirmed case in Korea was reported the following month in June.
In the second half of this year, the number of confirmed cases has decreased significantly, with a cumulative total of 155 patients and no deaths as of December 12.
On the other hand, classified as a sexually transmitted disease, syphilis' infectious disease status will be upgraded to Class 3 from Class 4 next year. According to the KDCA, the number of syphilis cases surged 10 percent year-on-year from February to July this year.
Syphilis is divided into stages 1 to 3 syphilis, latent syphilis, and congenital syphilis based on clinical symptoms.
The main symptom of stage 1 syphilis is a painless skin ulcer (chancre). In most cases, only one ulcer is observed, but there are cases of multiple sores.
Stage 2 syphilis is characterized by a rash on the skin and morbid symptoms on the mucous membranes. The rash appears several weeks after the painless sores that characterize stage 1 syphilis have healed.
Latent syphilis begins after the symptoms of stage 1 and stage 2 syphilis have disappeared, and if left untreated, the syphilis bacteria can remain in the body. This latent state can last for years.
Symptoms of stage 3 or late-stage syphilis are primarily internal organ damage and are caused by syphilis bacteria invading various organs, including the central nervous system, eyes, heart, large blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints.
In the case of neurosyphilis, which involves the central nervous system, symptoms may be asymptomatic, meningeal irritation, or cerebrovascular symptoms.
"The change in the infectious disease classification of syphilis will be implemented from next year following the revision of the relevant law," said a KDCA official. "There is a great concern that syphilis itself will progress more severely than other sexually transmitted infectious diseases."
"So far, we have been doing a good job of monitoring samples through designated organizations, but we have raised the grade to accurately identify the outbreak and respond properly," he added.
Related articles
- Korean mpox cases exceed 100, a year after 1st case
- Developers of mpox diagnostic kits, vaccines receive attention as mpox spreads in Korea
- Korea confirms 9th mpox patient with no history of overseas travel
- Korea confirms 3 new mpox cases in less than a week
- KDCA shifts to full monitoring of syphilis to prevent the spread

