European studies have once again confirmed the rising influence of artificial intelligence in early breast cancer detection, as Lunit, a Korean provider of AI-powered cancer diagnostic solutions, revealed findings from two large-scale studies on its mammography solution, Lunit INSIGHT MMG, on Wednesday.
Researchers from the Cancer Registry of Norway and Odense University Hospital in Denmark led these studies, demonstrating how Lunit’s AI can not only identify early-stage breast cancer but also predict future risks years in advance.
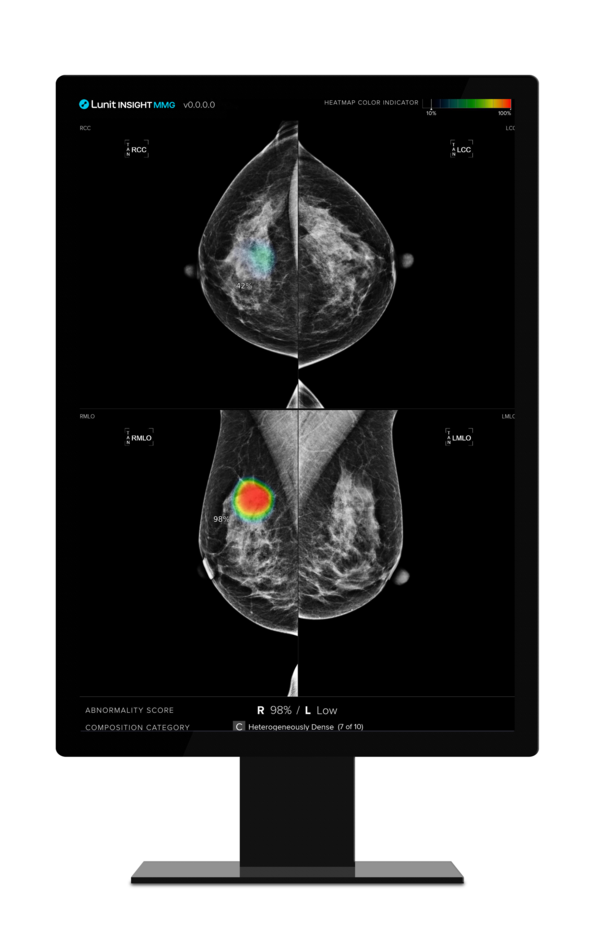
In Norway, Professor Solveig Hofvind’s team studied 116,495 women aged 50-69 who had undergone at least three rounds of biennial screening.
Published in JAMA Network Open on Oct. 3, the research revealed that Lunit's AI could foresee cancer risks as much as four to six years before conventional methods. Lunit INSIGHT MMG assigns a score from 0 to 100 for each breast, with higher scores indicating greater cancer likelihood. The study showed that AI scores for breasts developing cancer were consistently higher than those that remained cancer-free, with the gap widening over time
Lunit INSIGHT MMG assigns a score from 0 to 100 for each breast, with higher scores indicating a greater likelihood of cancer. The study showed that AI scores for breasts developing cancer were consistently higher than those that remained cancer-free, with the gap widening over time.
The AI’s ability to detect cancer improved across successive screenings, with the difference in scores between cancerous and non-cancerous breasts rising from 21.3 points in the first round to 79.0 by the third. By this stage, the AI’s accuracy in predicting cancer risk reached a near-perfect 0.96 in area under the curve (AUC) measurements.
"These findings highlight AI’s potential to transform personalized screening strategies," a Lunit spokesperson said, adding that the technology "opens new avenues for earlier interventions and more precise care."
Meanwhile, in Denmark, where double-reading mammograms are standard but labor-intensive, researchers explored how Lunit INSIGHT MMG could lighten the radiologists' workload without sacrificing accuracy. Dr. Mohammad T. Elhakim’s study, published in Radiology: Artificial Intelligence on Sept. 4, evaluated 249,402 mammograms, testing three different scenarios of AI-assisted screening.
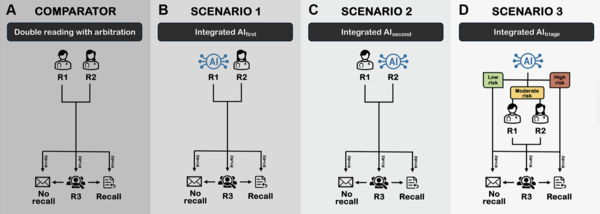
In the first scenario, AI replaced the first reader, cutting radiologists' workload by 48.8 percent while maintaining detection accuracy. In the second scenario, AI replaced the second reader, similarly reducing workload by 48.7 percent, though sensitivity dropped slightly by 1.5 percent.
The third and most effective approach saw AI triaging patients into high- and low-risk categories, trimming radiologist workloads by 49.7 percent while improving diagnostic accuracy. This approach, which minimized the need for case arbitration, also enhanced the positive predictive value and negative predictive value of screenings.
“This is a real-world solution to the resource crunch facing healthcare systems,” said a Lunit spokesperson, highlighting how AI can ease pressure on medical staff in countries facing personnel shortages. The spokesperson added that AI frees up radiologists to focus on the most complex cases without compromising the quality of care.
Brandon Suh, CEO of Lunit, called the findings “compelling evidence” of AI’s transformative potential. In Norway, where Lunit’s AI predicted cancer risk up to six years in advance, Suh emphasized how this early warning system gives women and doctors precious time for intervention. “These aren’t hypothetical improvements,” Suh noted. “They’re already benefiting patients today, and our goal is to ensure these advances translate into better outcomes for women undergoing breast cancer screening.”
Related articles
- Lunit to present AI-driven cancer treatment study at SITC 2024, selected for rapid oral presentation
- Lunit integrates AI solution into Roche Diagnostics' digital pathology platform
- Lunit’s AI biomarker predicts treatment response in bile duct cancer patients
- Lunit and Volpara to provide AI solutions to large US imaging platform
- Lunit's subsidiary Volpara signs software supply agreement with top US healthcare system
- Lunit’s subsidiary Volpara signs $7.3 million deal with US DHA for breast cancer screening software
- [SITC 2024] MD Anderson study shows Lunit SCOPE IO platform could transform immunotherapy selection
- 'High-intensity post-surgery imaging for breast cancer does not improve survival rates'
- Lunit partners with France's largest private medical imaging network to provide AI mammography
- Lunit shares soar over 20% on strategic AI pathology partnership with AstraZeneca
- Lunit to release 20 AI diagnostics studies at RSNA2024

