Korean researchers have solved one of the biggest challenges in the development of exosome-based therapeutics -- the problem of drug loading -- in a straightforward manner.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced on Wednesday that a team, led by Kim Ho-jun of its Biomolecular Recognition Research Center and Dr. Kim Hong-nam of the Brain Fusion Research Center, has developed a new drug loading technology that can quickly and stably load macromolecular drugs such as mRNA into exosomes.
Exosomes are biologically derived particles that transmit signals between cells and are attracting attention as a next-generation therapeutic delivery system for delivering drugs to specific cells. However, due to their rigid membrane structure, it is challenging to load large molecules, such as mRNA or proteins, inside. Previously, drugs were injected by electroshock or chemical treatment, but the efficiency was low, and the risk of damaging the exosomes or drugs was high, making it difficult to achieve.
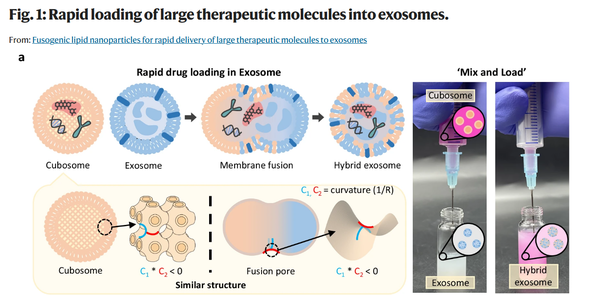
The team solved this problem by utilizing lipid nanoparticles called “cubosomes.” Cubosomes have a structure similar to cell membranes, naturally fuse with exosomes, and can stably encapsulate drugs of various sizes, including mRNA. By simply placing the mRNA-laden cubosomes and exosomes together for 10 minutes at room temperature, the team found that more than 98 percent of the mRNA was loaded into the exosomes, while the structure and function of the exosomes remained intact.
The exosomes successfully crossed the blood-brain barrier, a challenging barrier for drug delivery. They retained their “homing” properties, allowing them to return to the cells from which they were originally derived, confirming that they can deliver drugs precisely to the lesion site.
The team stated that this technology can be directly applied to the development of exosome-based therapeutics, eliminating the need for additional equipment or complex processes, thereby significantly enhancing its practical application potential. The researchers added that they plan to continue to evaluate the safety of the cubosome and secure a mass production system.
“This technology can be easily combined with exosomes and drugs in the medical field and used as a therapeutic agent, which is of great significance for the realization of customized therapies for patients,” Dr. Kim Ho-jun said.
Dr. Kim Hong-nam said, “It is possible to deliver drugs accurately even in complex tissues such as the brain, which could be used to treat various diseases.”
The paper, “Fusogenic lipid nanoparticles for rapid delivery of large therapeutic molecules to exosomes,” was published in the international journal Nature Communications.

