Lunit said on Thursday that a study published in the January 2023 issue of The Lancet Regional Health–Americas, demonstrated the effectiveness of Lunit’s INSIGHT CXR as a triage tool for tuberculosis (TB) screening in prisons.
Globally, prisons are high-risk settings for TB. In South America, TB cases in prisons have more than doubled since 2000 amid rising incarceration rates. Consequently, the World Health Organization (WHO) released updated guidelines in 2021 to recommend Lunit INSIGHT CXR as one of the computer-aided detection (CAD) software to aid TB screening and reduce physicians' manual screening.
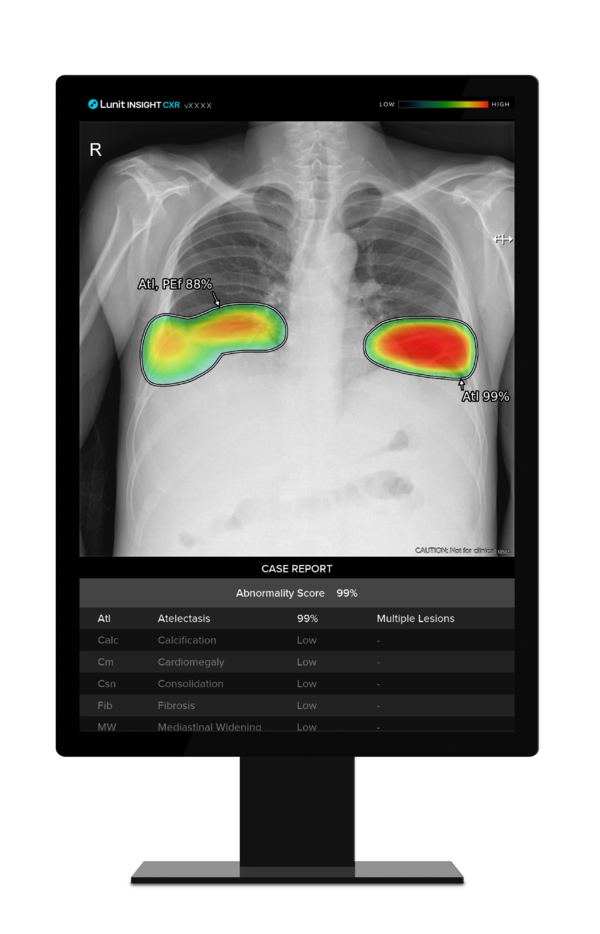
The AI solution detects suspicious lesions in chest x-ray images, helping radiologists identify disease areas by providing the location of the lesion with an abnormality score that reflects the AI’s confidence level. It can also detect the 10 most common chest abnormalities, including TB, with 97-99 percent accuracy.
The study, led by Dr. Julio Croda of the Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil, evaluated the accuracy of AI-based chest x-ray interpretation algorithms for TB screening in prisons with three commercially available x-ray algorithms, including Lunit INSIGHT CXR.
While all three algorithms performed similarly overall, Lunit INSIGHT CXR was among the only two algorithms that met WHO requirements for triage which refers to a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided due to a lack of resources, Lunit said.
The study also noted Lunit INSIGHT CXR as the best-performing algorithm among the cohort, showing greater accuracy and generalizability among subgroups, with superior specificity to age compared to others.
Furthermore, Lunit INSIGHT CXR was the only algorithm that met the WHO’s target product profile (TPP) criteria among individuals 45 years and older. A TPP outlines the desired characteristics of a target product like safety and efficacy that is aimed at a particular disease.
“The use of computer-aided detection (CAD) software is practical, inexpensive, and accurate for mass screening in populations with a high TB burden like in prisons,” said Dr. Julio Croda. “We observed a decrease in CAD specificity only in people who already had tuberculosis and so it is important to be cautious and also perform microbiological screening in these groups before making clinical decisions.”
Lunit CEO Brandon Suh also added that this study shows the value Lunit INSIGHT CXR can bring to prisons which are highly vulnerable to tuberculosis yet lacking diagnostic specialists.

