
"To prevent Covid-19 infection in the hospital, visits to the monitoring room will be banned from May 29, 2020."
That was a notice posted at a clinical trial center of a university hospital during the Covid-19 pandemic. As such, there have been a series of cases in which patients cannot visit clinical trial institutions due to restrictions on movement and quarantine during the period. That was not limited to domestic situations. Global clinical trials have also been suspended one after another.
All this revealed the limitation of existing clinical trials, where university hospitals or research organs directly evaluate results through a series of processes from recruiting clinical trial participants face-to-face, treating patients, and collecting data.
According to a survey by Vanson Bourne, a global pollster, on 400 executives in the clinical trial industry from the U.K., France, Germany, and Switzerland, 99 percent of respondents said the pandemic adversely affected the conduct of clinical trials. They cited such reasons as infection risks, work overload for medical professionals, and patients’ inability to visit hospitals.
What emerged as a solution against this backdrop was the Decentralized Clinical Trial. DCT, which can be summarized as hybrid, virtual, long distance, DtP (direct-to-patient), and direct delivery of clinical trial pharmaceutical products, collects clinical data using wearable or mobile devices and deliver trial drugs via mail, making clinical trial possible without participants visiting hospitals. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration defines DCT as clinical studies where part of all clinical trial-related activities are made in places other than where researchers are positioned.
Technological development changes ‘fixed concept’ of clinical trials
In short, DCA is a clinical trial getting out of clinical trial institutions. However, developing digital and other IT technology has made a new clinical trial possible.
More specifically, DCT draws attention because of easy recruitment of patients, convenience in conducting clinical trials, cost-effectiveness, data maintenance, and lower risks in and outside of institutions.
First, it is possible to quickly recruit the target number of people through various methods of participating in clinical trials, such as digital advertising, social media, patient organizations, direct advertising to the target audience, or the registry of the target audience. Subjects also can identify and register themselves with clinical studies of interest.
The patients recruited this way are more diverse and extensive than those gathered by conventional methods. Traditional clinical trials have limited distances around clinical institutions. However, as clinical trial subjects can apply remotely, patients with problems, such as long distances and restrictions in movement, can also participate in DCT.
Considering that the recruitment and registration of clinical trial subjects account for a significant portion of the clinical trial period, it is obvious that remote registration and participation of distant subjects will make it easy to activate the recruitment of subjects. For example, about 80 percent of clinical trials fail to meet the initial patient recruitment target. Given that the study begins only when the clinical trial registration is completed, even if the regulatory authorities approve the clinical trial, one can see the great effectiveness of DCT in recruiting patients.
Another advantage of DCT is that it increases the participation of clinical trial subjects. According to CenterWatch, a clinical study company, the average dropout rate in existing clinical trials reaches 30 percent. Considering the median cost per subject between 2015 and 2017 was $41,000, preventing dropouts is bound to increase cost-effectiveness.
Major reasons for the subject’s withdrawal are related to difficulty moving to research locations or inconvenience of trials, such as complexity in trial designs and data collection. In contrast, in DCT, subjects are connected to digital devices regardless of location. As a result, researchers can access participants' data anywhere, reducing the number of patient visits to the institutions during the clinical period.
In addition, DCT can reduce risks, such as safety, in developing new drugs. As it is based on remote monitoring, researchers can confirm the subjects’ biological information in real-time continually and persistently, even during periods when they don’t visit the institutions, managing the safety- and efficacy-related data.
When abnormal safety-related responses occurred previously, researchers could confirm only by the subjects’ visits or reports. Now, however, researchers can confirm them through remote monitoring in real-time and decide to discontinue drug administration more quickly.
Besides, they can improve the clinical trial design based on accumulated digital data, improving data quality and shortening its development period.
Rapid growth of DCT market reflects its efficiency
Interestingly, efforts had been made to overcome the shortcomings of existing clinical trials, if slowly, even before Covid-19’s outbreak, and such efforts expanded and quickened because of the pandemic.
According to GlobalData, the number of clinical trials using DCT increased by 13 percent in 2020 from the previous year and jumped by 57 percent in 2021 from 2020. The share of DCT also soared from 3.8 percent in 2015 to 11 percent in 2022 in the United States.
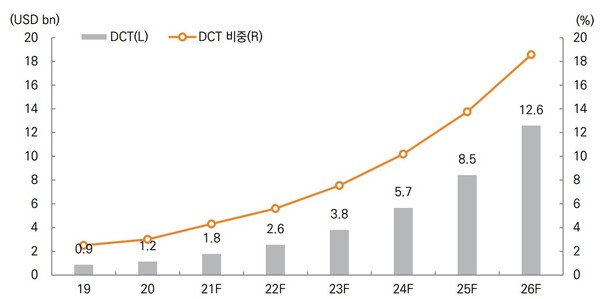
The global DCT market is growing even more rapidly. Mirae Asset Securities estimated the global DCT market at $2.59 billion in 2022 and will grow to $12.6 billion in 2026, accounting for 18.6 percent of the existing clinical trial market.
Contract research organizations (CROs) also carry out M&A and partnerships in keeping with the DCT trend. Typical examples include ICON’s acquisition of PRA at $12 billion in 2021 and the $8.5-billion acquisition of Parexel by EQT/Goldman Sachs.
The U.S. government is actively supporting new drug development using DCT. For example, in March 2020, the U.S. FDA included DCT in its guideline to protect researchers and patients during the Covid-19 pandemic. It also launched the Decentralized Trials & Research Alliance (DTRA) in December 2020.
Related articles
- [Special] 'Be it US, Europe, or China, DCT is global trend in clinical trials'
- [Special] DCT was behind 1st Covid-19 vaccine developed in just 1 year
- [Special] ‘Regulation’ blocks DCT introduction in Korea. So how to unravel tangled threads?
- Decentralized clinical trial emerges as irresistible trend. What about Korea?
- Clinical trials are shifting towards DCT but hybrid approach more likely: IQVIA execs
- Regulator ‘half-positive’ to digital healthcare firms' request to introduce DCTs
- JNP MEDI's pioneering role in DCT unveils enormous potential

